Identify Properties
Setting the Identify properties appropriately for a form set will improve the accuracy and speed of forms processing operations. To do this, first select the required form set within the Tree View and then open the Identify tab within the Properties View.
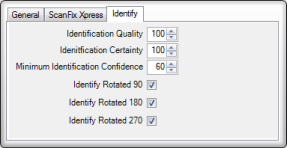
Identify tab in Properties View
Use the following guidelines to adjust your form set identification settings:
| Property | Description |
| Identification Quality |
The property controls the amount of effort that is expended in identifying an unknown image. Large values cause the identification process to explore more options in order to produce a more accurate and reliable result. Small values cause the identification process to take short-cuts in order to more quickly produce a result. There is no single, best value for this parameter. Instead, it depends on the values you place on accuracy and speed. In most cases, the value of accuracy is directly related to the cost of a human to review and correct problems. Many identification problems can be resolved by increasing the Identification Quality property. The default value is 50 and works in many instances. Increasing the value will improve the abilities and quality of the identification process and cause an increase in CPU time needed for each image. Some situations warrant a higher than normal value for this property. For example, if your form set includes many similar forms, you should increase this value. If your forms are small or have little form content, you should increase this value. Likewise, a few situations warrant a lower than normal value for this property. If your forms are all 8.5 x 11, with at least a dozen lines, and all substantially different from each other, you can lower this value and still get accurate results. |
| Identification Certainty |
This property indicates the probability that an unknown form is a match for a form in the form set. In most situations, you should set this property to 100, indicating that every unknown image should match a form in the form set. However, if you are processing mixed documents and some of the images do not represent forms, you should decrease this value. For example, if 15 of your images are cover letters or handwritten notes and 85 are forms, you should set this property to a value near 85. The precise value of this property is not very important. |
| Minimum Identification Confidence |
This property sets a minimum confidence for a successful match. If the best match for an unknown image has a confidence lower than this value, this object will never consider it a match. The Identify process contains a separate and independent internal minimum confidence and will also reject all matches that are lower than that value. The process bases that internal minimum confidence on several attributes, such as the Identification Certainty property, the Identification Quality, and the type of forms present in the form set. |
| Identify Rotated 90 |
This property controls comparison of rotated images. When this is checked, this object will rotate unknown images 90 degrees clockwise and check for a match against the templates in the given form set. Note that this rotated comparison is in addition to the normal, un-rotated comparison. If you know that your images are always rotated at a certain angle, you should un-rotate the images before you try to identify them. |
| Identify Rotated 180 |
This property controls comparison of rotated images. When this is checked, this object will rotate unknown images 180 degrees clockwise and check for a match against the templates in the given form set. Note that this rotated comparison is in addition to the normal, un-rotated comparison. If you know that your images are always rotated at a certain angle, you should un-rotate the images before you try to identify them. |
| Identify Rotated 270 |
This property controls comparison of rotated images. When this is checked, this object will rotate unknown images 270 degrees clockwise and check for a match against the templates in the given form set. Note that this rotated comparison is in addition to the normal, un-rotated comparison. If you know that your images are always rotated at a certain angle, you should un-rotate the images before you try to identify them. |